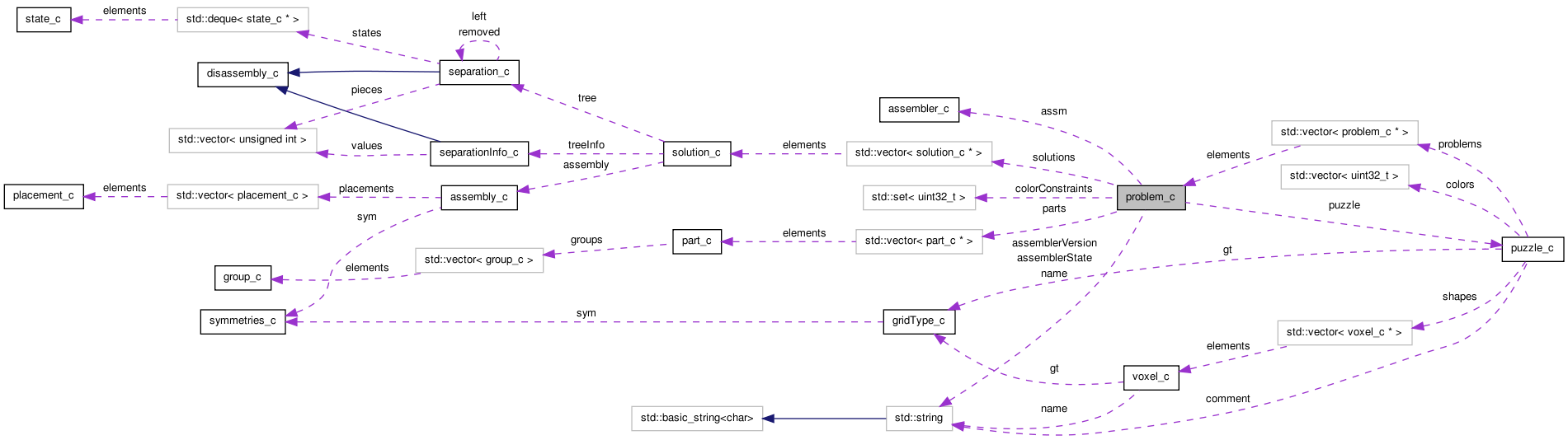
problem_c Class Reference
This class defines a problem,. More...
#include <problem.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| problem_c (puzzle_c &puz) | |
| constructor: create new empty problem for the given puzzle | |
| problem_c (puzzle_c &puz, xmlParser_c &pars) | |
| constructor: load a problem from the given XML node for the given puzzle | |
| problem_c (const problem_c *prob, puzzle_c &puz) | |
| constructor: copy the given problem, except for label and solutions | |
| ~problem_c (void) | |
| destructor: free all resources | |
| void | save (xmlWriter_c &xml) const |
| save the problem into the returned XML node | |
| const gridType_c * | getGridType (void) const |
| return the current set grid type for this puzzle. | |
| gridType_c * | getGridType (void) |
| return the current set grid type for this puzzle. | |
| const std::string & | getName (void) const |
| get the name of the problem. | |
| void | setName (std::string nm) |
| set the name of the problem. | |
| void | removeAllSolutions (void) |
| THE PROBLEM STATE. | |
Result shape handling | |
| void | setResultId (unsigned int shape) |
| set the puzzle shape id for the result shape. | |
| bool | resultValid (void) const |
| Check if there is a valid shape set. | |
| unsigned int | getResultId (void) const |
| Get the puzzle shape id for the result shape of the problem. | |
| const voxel_c * | getResultShape (void) const |
| get the voxel space of the result shape. | |
| voxel_c * | getResultShape (void) |
| get the voxel space of the result shape. | |
problem piece handling | |
a problem uses the shapes within the puzzle to define its pieces (you see the distinction, a shape is within the puzzle, a piece within the problem, there can be several pieces of the same shape) each shape has a min and max count attached to define how many times this shape is (may) be used.
You also need to separate the shape ID a shape has as index in the puzzle or the shape ID a shape as when it is the x-th shape in the problem. For example shape number 3 defined in the problem may be the first shape in the problem. TODO: try to find a proper name and interface to make sure this is done right. | |
| void | removeShape (unsigned short shapeId) |
| Remove the usage of a shape from a problem. | |
| void | setShapeMinimum (unsigned int shapeId, unsigned int count) |
| set the minimum number of times the shape may be used | |
| void | setShapeMaximum (unsigned int shapeId, unsigned int count) |
| set the maximum number of times the shape may be used | |
| unsigned int | getShapeMinimum (unsigned int shapeId) const |
| get the minimum number of times the shape may be used. | |
| unsigned int | getShapeMaximum (unsigned int shapeId) const |
| get the maximum number of times the piece may be used. | |
| bool | usesShape (unsigned int shapeId) const |
| find out, if a shape is used in the problem (as piece or as result) | |
| unsigned int | partNumber (void) const |
| how many different parts have been used in this problem. | |
| unsigned int | getShapeMin (unsigned int piece) const |
| get the minimum number of times a shape is used. | |
| unsigned int | getShapeMax (unsigned int piece) const |
| get the maximum number of times a shape is used. | |
| unsigned int | getShape (unsigned int piece) const |
| get the shape of a piece | |
| unsigned int | getShapeId (unsigned int shape) const |
| piece number that shape has in this problem | |
| const voxel_c * | getShapeShape (unsigned int piece) const |
| get the voxel space for a given piece | |
| voxel_c * | getShapeShape (unsigned int piece) |
| get the voxel space for a given piece | |
| void | exchangeShape (unsigned int p1, unsigned int p2) |
| swap the 2 pieces in the piece list of the problem | |
| void | exchangeShapeId (unsigned int s1, unsigned int s2) |
| the 2 shapes have been swapped in the puzzle, swap them here as well | |
find out what puzzle shape is behind a piece number in a given problem | |
| unsigned int | pieceNumber (void) const |
| find out how many pieces there are in this problem. | |
| unsigned int | pieceToShape (unsigned int pieceNr) const |
| find out which shape id (index in the problem shapes) is behind a given piece number | |
| unsigned int | pieceToSubShape (unsigned int pieceNr) const |
| find out the how manieth of a shape one piece is | |
edit color placement constraints. | |
the color 0 in this functions is always ignored as the placement of color 0 is always possible | |
| void | allowPlacement (unsigned int pc, unsigned int res) |
| allow placing pieces of one color into a result color | |
| void | disallowPlacement (unsigned int pc, unsigned int res) |
| disallow the placing | |
| bool | placementAllowed (unsigned int pc, unsigned int res) const |
| check if placing is allowed | |
grouping information. | |
these functions can be used to define groups that pieces belong to this information is used when disassembling the puzzle, if all pieces left in one clump belong to the same group the disassembler doesn't try to continue disassembling group 0 is different, it means that the piece doesn't belong to any group and must be single The problem with this are pieces with the same shape.
Each of this piece can belong into another group. But the assembler doesn't know about this and will only return one assembly. So the disassembler has to decide which piece belongs to what group all the | |
| void | setShapeGroup (unsigned int piece, unsigned short group, unsigned short count) |
| set the group and a count for the piece | |
| unsigned short | getShapeGroupNumber (unsigned int piece) const |
| get the number of groups that a piece is a member of | |
| unsigned short | getShapeGroup (unsigned int piece, unsigned int groupID) const |
| get the x-th group that a piece is a member of | |
| unsigned short | getShapeGroupCount (unsigned int piece, unsigned int groupID) const |
| find out how many instances of the piece may be a member of the x-th group | |
functions to limit the number of holes a solution is allowed to have. | |
| bool | maxHolesDefined (void) const |
| find out the the number is defined, if not there is no limit | |
| unsigned int | getMaxHoles (void) const |
| get the number (only when it is defined) | |
| void | setMaxHoles (unsigned int value) |
| set the number to a valid value | |
| void | setMaxHolesInvalid (void) |
| invalidate the value | |
functions used while solving the puzzle. | |
the assembler engine can be put into the problem to save it together with the problem and later on resume, or even to just pause solving when saved into XML only a string containing assembler dependent information is saved, this information is resurrected when setting the assembler | |
| assembler_c::errState | setAssembler (assembler_c *assm) |
| set the assembler. | |
| assembler_c * | getAssembler (void) |
| get the assembler | |
| const assembler_c * | getAssembler (void) const |
| get the assembler | |
| void | incNumAssemblies (void) |
| call this for each found assembly | |
| void | incNumSolutions (void) |
| call this for each found solution | |
| void | addTime (unsigned long time) |
| add time used to solve the puzzle (in seconds) the value is added to the already accumulated time. | |
| void | addSolution (assembly_c *assm) |
| add an assembly as a solution | |
| void | addSolution (assembly_c *assm, separationInfo_c *disasm, unsigned int pos=0xFFFFFFFF) |
| add an assembly with disassembly information as a solution. | |
| void | addSolution (assembly_c *assm, separation_c *disasm, unsigned int pos=0xFFFFFFFF) |
| add an assembly with disassembly proper as a solution. | |
| void | finishedSolving (void) |
| once finished analysing call finishedSolving for finish off all actions. | |
| void | makeUnknown (void) |
| transfer the problem into the unknown state | |
functions used after solving to get information. | |
For each analysis some information is saved: the number of assemblies and solutions and the time required for the analysis.
Additionally some or all of the found solutions may be saved. Information about those solutions can be acquired. Each of those saved solutions also has some information attached: the assembly and solution number | |
| solveState_e | getSolveState (void) const |
| find out how far we are with solving (no, started, finished) | |
| bool | numAssembliesKnown (void) const |
| find out if we have an idea about the number of assemblies | |
| unsigned long | getNumAssemblies (void) const |
| get number of assemblies found so far. | |
| bool | numSolutionsKnown (void) const |
| find out if we have an idea about the number of solutions | |
| unsigned long | getNumSolutions (void) const |
| get number of solutions found so far. | |
| bool | usedTimeKnown (void) const |
| find out, if we know something about the time for solving the puzzle | |
| unsigned long | getUsedTime (void) const |
| find out the time used to solve the puzzle up to the current state. | |
| unsigned int | solutionNumber (void) const |
| get number of solutions that were stored | |
| const solution_c * | getSolution (unsigned int sol) const |
| solution_c * | getSolution (unsigned int sol) |
organize solutions | |
| void | removeSolution (unsigned int sol) |
| remove the i-th solution from the solution list | |
| void | sortSolutions (int by) |
| sort solutions by 0=assembly, 1=level, 2=sumMoves, 3=pieces | |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | editProblem (void) |
| called, when the problem gets changed | |
| problem_c (const problem_c &) | |
| void | operator= (const problem_c &) |
Private Attributes | |
| puzzle_c & | puzzle |
| the puzzle this problem belongs to, it must always be there | |
| std::vector< part_c * > | parts |
| the pieces for this problem and how many of the pieces of each shape are there, the shape class contains indices into the shape list of the puzzle and some counters, . | |
| unsigned int | result |
| the result shape shape as index into the puzzle shapes | |
| std::vector< solution_c * > | solutions |
| (some of) the found solutions. | |
| std::set< uint32_t > | colorConstraints |
| this set contains the pairs of colours that are allowed when a piece is placed. | |
| assembler_c * | assm |
| if we have started to solve this problem this pointer shows us the corresponding assembler if the pointer is 0 we have never started an assembly process within this session statistics can be found in the assembler, too | |
| std::string | name |
| the name of the problem, so that the user can easily select one out of a list with names | |
| solveState_e | solveState |
| this state reflects how far we are with solving this problem | |
| unsigned long | numAssemblies |
| Number of found assemblies for the problem. | |
| unsigned long | numSolutions |
| Number of found solutions for the problem. | |
| std::string | assemblerState |
| we only save the information that the assembler needs to reset it's state and use this information once the user wants to continue solving the problem otherwise the loading might take quite a while | |
| std::string | assemblerVersion |
| each assembler also saves a version into the node so that it can check, if the saves state can be restored | |
| unsigned long | usedTime |
| the time used up to get to the current state in the solving progress (in seconds) | |
| unsigned int | maxHoles |
| number of holes maximally allowed this value *may* be used to limit the number of holes, if you have piece ranges in your puzzle. | |
Detailed Description
This class defines a problem,.It always has to belong to a puzzle and can not be put somewhere else. A puzzle is a collection of shapes and a set of problems associated with these shapes each problem defines a solution shape and a set of pieces (multiple occurrences are possible) that need to be assembles into the given solution shape the class also handles the solutions that belong to the problem
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| problem_c::problem_c | ( | puzzle_c & | puz | ) |
constructor: create new empty problem for the given puzzle
| problem_c::problem_c | ( | puzzle_c & | puz, | |
| xmlParser_c & | pars | |||
| ) |
constructor: load a problem from the given XML node for the given puzzle
References assemblerState, assemblerVersion, colorConstraints, xmlParser_c::END_TAG, xmlParser_c::exception(), xmlParser_c::getAttributeValue(), puzzle_c::getGridType(), xmlParser_c::getName(), xmlParser_c::getText(), max(), maxHoles, min(), name, xmlParser_c::next(), xmlParser_c::nextTag(), numAssemblies, numSolutions, parts, puzzle, xmlParser_c::require(), result, puzzle_c::shapeNumber(), xmlParser_c::skipSubTree(), solutions, solveState, SS_UNSOLVED, xmlParser_c::START_TAG, and usedTime.
constructor: copy the given problem, except for label and solutions
References assm, colorConstraints, maxHoles, and parts.
| problem_c::~problem_c | ( | void | ) |
| problem_c::problem_c | ( | const problem_c & | ) | [private] |
Member Function Documentation
| void problem_c::addSolution | ( | assembly_c * | assm, | |
| separation_c * | disasm, | |||
| unsigned int | pos = 0xFFFFFFFF | |||
| ) |
add an assembly with disassembly proper as a solution.
You can give the index, where to add it. This defaults to the end of the list
References bt_assert, numAssemblies, numSolutions, solutions, solveState, and SS_SOLVING.
| void problem_c::addSolution | ( | assembly_c * | assm, | |
| separationInfo_c * | disasm, | |||
| unsigned int | pos = 0xFFFFFFFF | |||
| ) |
add an assembly with disassembly information as a solution.
You can give the index, where to add it. This defaults to the end of the list
References bt_assert, numAssemblies, numSolutions, solutions, solveState, and SS_SOLVING.
| void problem_c::addSolution | ( | assembly_c * | assm | ) |
add an assembly as a solution
References bt_assert, numAssemblies, solutions, solveState, and SS_SOLVING.
Referenced by solveThread_c::assembly().
| void problem_c::addTime | ( | unsigned long | time | ) | [inline] |
add time used to solve the puzzle (in seconds) the value is added to the already accumulated time.
References bt_assert, solveState, SS_SOLVING, and usedTime.
Referenced by solveThread_c::run().
| void problem_c::allowPlacement | ( | unsigned int | pc, | |
| unsigned int | res | |||
| ) |
allow placing pieces of one color into a result color
References bt_assert, colorConstraints, puzzle_c::colorNumber(), and puzzle.
| void problem_c::disallowPlacement | ( | unsigned int | pc, | |
| unsigned int | res | |||
| ) |
| void problem_c::editProblem | ( | void | ) | [private] |
called, when the problem gets changed
References makeUnknown(), solveState, SS_SOLVED, and SS_SOLVING.
Referenced by removeShape(), setShapeMaximum(), and setShapeMinimum().
| void problem_c::exchangeShape | ( | unsigned int | p1, | |
| unsigned int | p2 | |||
| ) |
| void problem_c::exchangeShapeId | ( | unsigned int | s1, | |
| unsigned int | s2 | |||
| ) |
| void problem_c::finishedSolving | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
once finished analysing call finishedSolving for finish off all actions.
After that call no more modifications are possible, no more addSOlution, incNumAssemblies and so on.
References solveState, and SS_SOLVED.
Referenced by solveThread_c::run().
| const assembler_c* problem_c::getAssembler | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
| assembler_c* problem_c::getAssembler | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
| gridType_c * problem_c::getGridType | ( | void | ) |
return the current set grid type for this puzzle.
the grid type is taken from the puzzle this problem belongs to
References puzzle_c::getGridType(), and puzzle.
| const gridType_c * problem_c::getGridType | ( | void | ) | const |
return the current set grid type for this puzzle.
the grid type is taken from the puzzle this problem belongs to
References puzzle_c::getGridType(), and puzzle.
Referenced by assembly_c::createSpace(), assembler_1_c::getAssembly(), assembler_0_c::getAssembly(), movementAnalysator_c::movementAnalysator_c(), movementCache_c::movementCache_c(), assembler_1_c::prepare(), assembler_0_c::prepare(), print(), and solveThread_c::run().
| unsigned int problem_c::getMaxHoles | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
get the number (only when it is defined)
References bt_assert, and maxHoles.
Referenced by assembler_1_c::createMatrix().
| const std::string& problem_c::getName | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
| unsigned long problem_c::getNumAssemblies | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
get number of assemblies found so far.
Throws an exception, when not known
References bt_assert, numAssemblies, solveState, and SS_UNSOLVED.
Referenced by solveThread_c::assembly(), and solveThread_c::start().
| unsigned long problem_c::getNumSolutions | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
get number of solutions found so far.
Throws an exception, when not known
References bt_assert, numSolutions, solveState, and SS_UNSOLVED.
Referenced by solveThread_c::assembly(), and solveThread_c::start().
| unsigned int problem_c::getResultId | ( | void | ) | const |
Get the puzzle shape id for the result shape of the problem.
Make sure to only call getResultId[Shape] when you know that the shape is valid
References bt_assert, puzzle, result, and puzzle_c::shapeNumber().
Referenced by print().
| voxel_c * problem_c::getResultShape | ( | void | ) |
get the voxel space of the result shape.
Make sure to only call getResultId[Shape] when you know that the shape is valid
References bt_assert, puzzle_c::getShape(), puzzle, result, and puzzle_c::shapeNumber().
| const voxel_c * problem_c::getResultShape | ( | void | ) | const |
get the voxel space of the result shape.
Make sure to only call getResultId[Shape] when you know that the shape is valid
References bt_assert, puzzle_c::getShape(), puzzle, result, and puzzle_c::shapeNumber().
Referenced by assembler_1_c::canPlace(), assembler_0_c::canPlace(), assembler_1_c::createMatrix(), assembler_0_c::createMatrix(), assembler_1_c::prepare(), assembler_0_c::prepare(), print(), assembly_c::smallerRotationExists(), and assembly_c::transform().
| unsigned int problem_c::getShape | ( | unsigned int | piece | ) | const |
get the shape of a piece
References bt_assert, and parts.
Referenced by disassembler_a_c::disassembler_a_c(), loadPuzzlerSolver3D(), assembler_1_c::prepare(), assembler_0_c::prepare(), and print().
| unsigned short problem_c::getShapeGroup | ( | unsigned int | piece, | |
| unsigned int | groupID | |||
| ) | const |
get the x-th group that a piece is a member of
References bt_assert, and parts.
Referenced by disassembler_a_c::disassembler_a_c(), and disassembler_a_c::subProbGroup().
| unsigned short problem_c::getShapeGroupCount | ( | unsigned int | piece, | |
| unsigned int | groupID | |||
| ) | const |
find out how many instances of the piece may be a member of the x-th group
References bt_assert, and parts.
Referenced by disassembler_a_c::disassembler_a_c().
| unsigned short problem_c::getShapeGroupNumber | ( | unsigned int | piece | ) | const |
get the number of groups that a piece is a member of
References bt_assert, and parts.
Referenced by disassembler_a_c::disassembler_a_c(), and disassembler_a_c::subProbGroup().
| unsigned int problem_c::getShapeId | ( | unsigned int | shape | ) | const |
piece number that shape has in this problem
References bt_assert, parts, puzzle, and puzzle_c::shapeNumber().
| unsigned int problem_c::getShapeMax | ( | unsigned int | piece | ) | const |
get the maximum number of times a shape is used.
This similar as the getShapeMinimum function but this time the piece index instead of the shape index
References bt_assert, and parts.
Referenced by assembler_0_c::canHandle(), assembler_1_c::createMatrix(), disassembler_a_c::disassembler_a_c(), assembler_1_c::getPiecePlacement(), assembler_1_c::getPiecePlacementCount(), movementAnalysator_c::movementAnalysator_c(), movementCache_c::movementCache_c(), assembler_1_c::prepare(), print(), assembly_c::sort(), assembly_c::transform(), and assembly_c::validSolution().
| unsigned int problem_c::getShapeMaximum | ( | unsigned int | shapeId | ) | const |
get the maximum number of times the piece may be used.
if the shape is not used in the problem, the function returns 0
References bt_assert, parts, puzzle, and puzzle_c::shapeNumber().
Referenced by loadPuzzlerSolver3D().
| unsigned int problem_c::getShapeMin | ( | unsigned int | piece | ) | const |
get the minimum number of times a shape is used.
This similar as the getShapeMinimum function but this time the piece index instead of the shape index
References bt_assert, and parts.
Referenced by assembler_0_c::canHandle(), assembler_1_c::createMatrix(), assembler_1_c::prepare(), and print().
| unsigned int problem_c::getShapeMinimum | ( | unsigned int | shapeId | ) | const |
get the minimum number of times the shape may be used.
if the shape is not used in the problem, the function returns 0
References bt_assert, parts, puzzle, and puzzle_c::shapeNumber().
Referenced by loadPuzzlerSolver3D().
| voxel_c * problem_c::getShapeShape | ( | unsigned int | piece | ) |
get the voxel space for a given piece
References bt_assert, puzzle_c::getShape(), parts, and puzzle.
| const voxel_c * problem_c::getShapeShape | ( | unsigned int | piece | ) | const |
get the voxel space for a given piece
References bt_assert, puzzle_c::getShape(), parts, and puzzle.
Referenced by assembler_1_c::createMatrix(), assembler_0_c::createMatrix(), assembly_c::createSpace(), loadPuzzlerSolver3D(), movementAnalysator_c::movementAnalysator_c(), movementCache_c::movementCache_c(), assembler_1_c::prepare(), assembler_0_c::prepare(), print(), and assembly_c::transform().
| solution_c* problem_c::getSolution | ( | unsigned int | sol | ) | [inline] |
| const solution_c* problem_c::getSolution | ( | unsigned int | sol | ) | const [inline] |
| solveState_e problem_c::getSolveState | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
| unsigned long problem_c::getUsedTime | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
find out the time used to solve the puzzle up to the current state.
Throws an exception when unknown
References bt_assert, solveState, SS_UNSOLVED, and usedTime.
| void problem_c::incNumAssemblies | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
call this for each found assembly
References bt_assert, numAssemblies, solveState, and SS_SOLVING.
Referenced by solveThread_c::assembly().
| void problem_c::incNumSolutions | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
call this for each found solution
References bt_assert, numSolutions, solveState, and SS_SOLVING.
Referenced by solveThread_c::assembly().
| void problem_c::makeUnknown | ( | void | ) |
transfer the problem into the unknown state
References assemblerState, assemblerVersion, assm, numAssemblies, numSolutions, solveState, SS_UNKNOWN, and usedTime.
Referenced by editProblem().
| bool problem_c::maxHolesDefined | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
find out the the number is defined, if not there is no limit
References maxHoles.
Referenced by assembler_1_c::createMatrix().
| bool problem_c::numAssembliesKnown | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
find out if we have an idea about the number of assemblies
References solveState, and SS_UNSOLVED.
Referenced by solveThread_c::start().
| bool problem_c::numSolutionsKnown | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
find out if we have an idea about the number of solutions
References solveState, and SS_UNSOLVED.
Referenced by solveThread_c::start().
| void problem_c::operator= | ( | const problem_c & | ) | [private] |
| unsigned int problem_c::partNumber | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
how many different parts have been used in this problem.
This is NOT the number of pieces in the problem
References parts.
Referenced by assembler_0_c::canHandle(), assembler_1_c::createMatrix(), assembler_0_c::createMatrix(), disassembler_a_c::disassembler_a_c(), assembler_1_c::getAssembly(), loadPuzzlerSolver3D(), movementAnalysator_c::movementAnalysator_c(), movementCache_c::movementCache_c(), assembler_1_c::prepare(), assembler_0_c::prepare(), print(), assembly_c::sort(), assembly_c::transform(), and assembly_c::validSolution().
| unsigned int problem_c::pieceNumber | ( | void | ) | const |
find out how many pieces there are in this problem.
This is the maximum valid value for the other 2 functions in this group
References max(), parts, and result.
Referenced by assembler_1_c::createMatrix(), assembler_0_c::createMatrix(), disassembler_a_c::disassemble(), disassembler_a_c::disassembler_a_c(), movementAnalysator_c::movementAnalysator_c(), movementCache_c::movementCache_c(), assembler_1_c::prepare(), assembler_0_c::prepare(), and setShapeMinimum().
| unsigned int problem_c::pieceToShape | ( | unsigned int | pieceNr | ) | const |
find out which shape id (index in the problem shapes) is behind a given piece number
References bt_assert, max(), and parts.
Referenced by assembly_c::createSpace().
| unsigned int problem_c::pieceToSubShape | ( | unsigned int | pieceNr | ) | const |
| bool problem_c::placementAllowed | ( | unsigned int | pc, | |
| unsigned int | res | |||
| ) | const |
check if placing is allowed
References bt_assert, colorConstraints, puzzle_c::colorNumber(), and puzzle.
Referenced by assembler_1_c::canPlace(), assembler_0_c::canPlace(), and assembly_c::smallerRotationExists().
| void problem_c::removeAllSolutions | ( | void | ) |
THE PROBLEM STATE.
a problem has 4 states: SS_UNSOLVED: fresh puzzle, no solving done SS_SOLVING: solving is in progress, an assembler is present SS_SOLVED: solving has been done, assembly and solution numbers are correct SS_FREESTYLE: no assembler, no assembly and solution number, but some solutions are present
you normally start out in SS_UNSOLVED, then start solving and end in solved and then you can reset to unsolved. when you do some editing in solving or in solved state you will end up un FREESTYLE because the already gathered information is likely to be incomplete, but as it is not completely wrong we simply keep it
the function resetToUnsolved will reset the problem into the unsolved state, drop all solutions and remove all information Then you call startSolving and progress to solving state Finally finished Solving will end you in solved state There are a lot of other functions that can make you end up in freestyle mode... remove all known solutions, reset time, counter, assembler. prepare for solving the problem it also removes maybe saved assembler state so that solving starts from the start
References assemblerState, assm, numAssemblies, numSolutions, solutions, solveState, SS_UNSOLVED, and usedTime.
Referenced by solveThread_c::run(), and setResultId().
| void problem_c::removeShape | ( | unsigned short | shapeId | ) |
Remove the usage of a shape from a problem.
when a shape is removed from the puzzle this function is called, it removes all ocurences of this shape in the problem and also updates the indices because the larger ones have shifted.
idx is the shape id form the puzzle, not the index of the shape in the problem.
References editProblem(), parts, result, and setShapeMaximum().
| void problem_c::removeSolution | ( | unsigned int | sol | ) |
remove the i-th solution from the solution list
References bt_assert, and solutions.
Referenced by solveThread_c::assembly().
| bool problem_c::resultValid | ( | void | ) | const |
Check if there is a valid shape set.
References puzzle, result, and puzzle_c::shapeNumber().
Referenced by assembler_1_c::createMatrix(), assembler_0_c::createMatrix(), and print().
| void problem_c::save | ( | xmlWriter_c & | xml | ) | const |
save the problem into the returned XML node
References xmlWriter_c::addContent(), assemblerState, assemblerVersion, assm, colorConstraints, xmlWriter_c::endTag(), max(), maxHoles, min(), name, xmlWriter_c::newAttrib(), xmlWriter_c::newTag(), numAssemblies, numSolutions, parts, result, assembler_c::save(), solutions, solveState, SS_SOLVING, SS_UNSOLVED, and usedTime.
| assembler_c::errState problem_c::setAssembler | ( | assembler_c * | assm | ) |
set the assembler.
The set assembler will be reset to a saved state, when that information is available. If not simply set the assembler
References assemblerState, assemblerVersion, bt_assert, assembler_c::ERR_NONE, numAssemblies, numSolutions, assembler_c::setPosition(), solveState, SS_SOLVING, and SS_UNSOLVED.
Referenced by solveThread_c::run().
| void problem_c::setMaxHoles | ( | unsigned int | value | ) | [inline] |
| void problem_c::setMaxHolesInvalid | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
| void problem_c::setName | ( | std::string | nm | ) | [inline] |
| void problem_c::setResultId | ( | unsigned int | shape | ) |
set the puzzle shape id for the result shape.
Make sure that it is valid in the puzzle before this function is called the result shape might be invalid
References bt_assert, puzzle, removeAllSolutions(), result, and puzzle_c::shapeNumber().
Referenced by loadPuzzlerSolver3D().
| void problem_c::setShapeGroup | ( | unsigned int | piece, | |
| unsigned short | group, | |||
| unsigned short | count | |||
| ) |
| void problem_c::setShapeMaximum | ( | unsigned int | shapeId, | |
| unsigned int | count | |||
| ) |
set the maximum number of times the shape may be used
References bt_assert, editProblem(), max(), min(), parts, puzzle, setShapeMinimum(), puzzle_c::shapeNumber(), and solutions.
Referenced by loadPuzzlerSolver3D(), removeShape(), and setShapeMinimum().
| void problem_c::setShapeMinimum | ( | unsigned int | shapeId, | |
| unsigned int | count | |||
| ) |
set the minimum number of times the shape may be used
References bt_assert, editProblem(), max(), min(), parts, pieceNumber(), puzzle, setShapeMaximum(), puzzle_c::shapeNumber(), and solutions.
Referenced by loadPuzzlerSolver3D(), and setShapeMaximum().
| unsigned int problem_c::solutionNumber | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
get number of solutions that were stored
References solutions.
Referenced by solveThread_c::assembly().
| void problem_c::sortSolutions | ( | int | by | ) |
sort solutions by 0=assembly, 1=level, 2=sumMoves, 3=pieces
References comp_0_assembly(), comp_1_level(), comp_2_moves(), comp_3_pieces(), and solutions.
| bool problem_c::usedTimeKnown | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
find out, if we know something about the time for solving the puzzle
References solveState, and SS_UNSOLVED.
| bool problem_c::usesShape | ( | unsigned int | shapeId | ) | const |
Member Data Documentation
std::string problem_c::assemblerState [private] |
we only save the information that the assembler needs to reset it's state and use this information once the user wants to continue solving the problem otherwise the loading might take quite a while
Referenced by makeUnknown(), problem_c(), removeAllSolutions(), save(), and setAssembler().
std::string problem_c::assemblerVersion [private] |
each assembler also saves a version into the node so that it can check, if the saves state can be restored
Referenced by makeUnknown(), problem_c(), save(), and setAssembler().
assembler_c* problem_c::assm [private] |
if we have started to solve this problem this pointer shows us the corresponding assembler if the pointer is 0 we have never started an assembly process within this session statistics can be found in the assembler, too
Referenced by getAssembler(), makeUnknown(), problem_c(), removeAllSolutions(), save(), and ~problem_c().
std::set<uint32_t> problem_c::colorConstraints [private] |
this set contains the pairs of colours that are allowed when a piece is placed.
The piece colour is in the high 16 bits, the result colour in the lower 16. As right now only 64 colours are possible this will allow enough space for the future
Referenced by allowPlacement(), disallowPlacement(), placementAllowed(), problem_c(), and save().
unsigned int problem_c::maxHoles [private] |
number of holes maximally allowed this value *may* be used to limit the number of holes, if you have piece ranges in your puzzle.
As soon as there are no piece ranges, this value can be calculated exactly and there is no need to limit the number the value 0xFFFFFFFF is used for undefined maximum number
Referenced by getMaxHoles(), maxHolesDefined(), problem_c(), save(), setMaxHoles(), and setMaxHolesInvalid().
std::string problem_c::name [private] |
the name of the problem, so that the user can easily select one out of a list with names
Referenced by getName(), problem_c(), save(), and setName().
unsigned long problem_c::numAssemblies [private] |
Number of found assemblies for the problem.
this is independent of the solutions vector, these are the pure numbers. 0xFFFFFFFF stands for too many to count
Referenced by addSolution(), getNumAssemblies(), incNumAssemblies(), makeUnknown(), problem_c(), removeAllSolutions(), save(), and setAssembler().
unsigned long problem_c::numSolutions [private] |
Number of found solutions for the problem.
this is independent of the solutions vector, these are the pure numbers. 0xFFFFFFFF stands for too many to count
Referenced by addSolution(), getNumSolutions(), incNumSolutions(), makeUnknown(), problem_c(), removeAllSolutions(), save(), and setAssembler().
std::vector<part_c *> problem_c::parts [private] |
the pieces for this problem and how many of the pieces of each shape are there, the shape class contains indices into the shape list of the puzzle and some counters, .
..
Referenced by exchangeShape(), exchangeShapeId(), getShape(), getShapeGroup(), getShapeGroupCount(), getShapeGroupNumber(), getShapeId(), getShapeMax(), getShapeMaximum(), getShapeMin(), getShapeMinimum(), getShapeShape(), partNumber(), pieceNumber(), pieceToShape(), pieceToSubShape(), problem_c(), removeShape(), save(), setShapeGroup(), setShapeMaximum(), setShapeMinimum(), usesShape(), and ~problem_c().
puzzle_c& problem_c::puzzle [private] |
the puzzle this problem belongs to, it must always be there
Referenced by allowPlacement(), disallowPlacement(), getGridType(), getResultId(), getResultShape(), getShapeId(), getShapeMaximum(), getShapeMinimum(), getShapeShape(), placementAllowed(), problem_c(), resultValid(), setResultId(), setShapeMaximum(), and setShapeMinimum().
unsigned int problem_c::result [private] |
the result shape shape as index into the puzzle shapes
Referenced by exchangeShapeId(), getResultId(), getResultShape(), pieceNumber(), problem_c(), removeShape(), resultValid(), save(), setResultId(), and usesShape().
std::vector<solution_c*> problem_c::solutions [private] |
(some of) the found solutions.
Not all of even none might be in this vector if the user decides to only count, or not keep them all. This vector contains the solutions that were kept
Referenced by addSolution(), exchangeShape(), getSolution(), problem_c(), removeAllSolutions(), removeSolution(), save(), setShapeMaximum(), setShapeMinimum(), solutionNumber(), sortSolutions(), and ~problem_c().
solveState_e problem_c::solveState [private] |
this state reflects how far we are with solving this problem
Referenced by addSolution(), addTime(), editProblem(), finishedSolving(), getNumAssemblies(), getNumSolutions(), getSolveState(), getUsedTime(), incNumAssemblies(), incNumSolutions(), makeUnknown(), numAssembliesKnown(), numSolutionsKnown(), problem_c(), removeAllSolutions(), save(), setAssembler(), and usedTimeKnown().
unsigned long problem_c::usedTime [private] |
the time used up to get to the current state in the solving progress (in seconds)
Referenced by addTime(), getUsedTime(), makeUnknown(), problem_c(), removeAllSolutions(), and save().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- src/lib/problem.h
- src/lib/problem.cpp
 1.5.8
1.5.8