Contents
Previous
Next
When using the main menu entry Status a window (Figure
WindowStatus) like the one above opens
and displays all kinds of information about all the shapes available
inside the puzzle. The table columns have the following meanings:
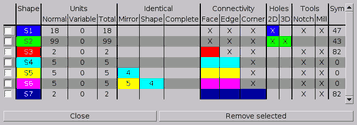
Figure: The Status window
- Units Normal
- Contains the number of voxels inside the shape that have the state
fixed.
- Units Variable
- Contains the number of voxel inside the shape that have the state
variable.
- Units Total
- Contains the number of voxels inside the shape that are either
fixed or variable.
- Identical
- If the shape is identical to another shape with smaller number, the
first such number is displayed; so if shape 3, 4, and 5 are identical,
shape 4 and 5 will point to shape 3 but shape 3 will show no
indication.
- Identical Mirror
- A previous shape is cited, if the shapes can somehow be transformed
into the other including the mirror transformation.
- Identical Shape
- A previous shape is cited, if the shapes are identical without
mirroring.
- Identical Complete
- In this case shapes must be completely identical including colours
and not only the appearance of the shape.
- Connectivity
- This part of the table shows if the shape is completely connected,
i.e. doesn't contain any separate voxels.
- Connectivity Face
- This part is marked with an X when all parts of the shape are
connected via the faces of the voxels. A face is a surface of a voxel.
Cubes have 6 such faces, the triangular voxels have 5, and spheres have
12 faces.
- Connectivity Edge
- This part is marked with an X when all parts of the shape are
connected via an edge or a face of the voxel. An edge is the connection
between 2 corners of a voxel. A cube has 12 edges and the triangular
voxel have 9. Spheres have no edges.
- Connectivity Corner
- This part is marked with an X when all parts of the shape are
connected via a corner, an edge, or a face. A corner is the end of an
edge. Cubes have 8 corners, the triangular voxel have 6 corners, and
spheres have none.
- Holes
- This part of the table contains information about possible holes
inside the shapes.
- Holes 2D
- A 2D hole is a hole in a 2-dimensional shape. So the o-octomino has
a 2D hole.
- Holes 3D
- A 3D hole is a completely surrounded region inside a shape.
- Sym
- This is a column that is mainly there for my help. BURRTOOLS needs
to know about all kinds of symmetries a shape can have. If a shape
turns up that has a kind of symmetry yet unknown to the program it
cannot solve puzzles with this shape. So here is a tool to check
beforehand and without the need to create a problem. If you ever see a
coloured mark in the last column send me the shapes where it turns up.
As long as this last column contains only numbers without a coloured
mark everything is fine.
Because calculating all this information can take a considerable
amount of time, BURRTOOLS pops up a window when it is working on
accumulating this table. The window contains a progress bar to guess
how much longer it will take. There is also a Cancel button at
the bottom that lets you abort this calculation and view the results
already gathered.
Contents
Previous
Next

